02 JDK NIO原理和关键类分析

什么是NIO
在介绍Netty之前,首先学习下什么是NIO是非常有必要的。有的地方称NIO为新I/O(New Input Output),原因是相对于之前版本的I/O库而言,它是一种新增的I/O模型,这也是官方的叫法。有的又称之为非堵塞I/O(Non-Blocking Input Output),因为相对于之前的传统的I/O模型来说,它设计的目标就是让java支持非堵塞I/O,所以很多场景下又有人称之为非堵塞I/O。个人理解堵塞和非堵塞的叫法主要是体现在read数据层面,称之为非堵塞I/O更合适。接下来学习NIO中在java层面包含哪些类,这些类之间又是如何实现的功能的。
Java NIO核心类
Selector
A multiplexor of {@link SelectableChannel} objects.Selector 是针对SelectableChannel对象的多路复用器,SelectableChannel将相关事件注册到Selector上,随后Selector通过轮询SelectableChannel,判断SelectableChannel是否有存在就绪事件。如果存在,则通过SelectionKey获取相应Selector和SelectableChannel,执行相关事件逻辑。
一个多路复用器可以注册多个SelectChannel,其原理图如下所示:
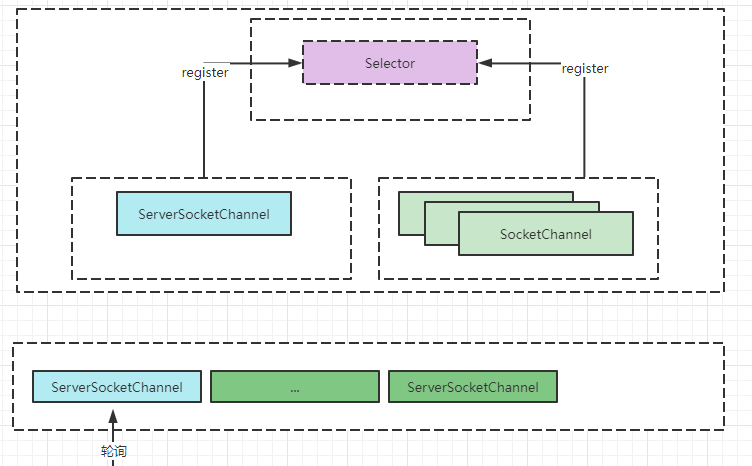
注册的SelectableChannel包含ServerSocketChannel和多个SocketChannel,Selector通过不断地轮询出注册的就绪事件。所谓就绪事件是指可以进行数据的读取或者数据的写出或者有客户端链接(轮询的方式有select、poll以及epoll ,不同的轮询方式低层对应的数据结构也不同)。
核心API
核心API功能介绍如下
//创建一个Selector方法 public static Selector open() throws IOException { return SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector(); } /** 判断当前Selector是否打开,打开方可使用,如上openSelector */ public abstract boolean isOpen(); //创建Selector的Provider public abstract SelectorProvider provider(); // 注册的所有事件 public abstract Set<SelectionKey> keys(); //注册的所有就绪事件 public abstract Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys(); // 查询是否有就绪事件且立刻方法 public abstract int selectNow() throws IOException; //查询是否有 public abstract int select(long timeout) throws IOException; // 查询是否有就绪的事件,如果没有,则当前调用的线程一直会被堵塞 public abstract int select() throws IOException; // 唤醒当前线程被select()或者select(long timeout)的线程 public abstract Selector wakeup(); // 关闭轮询,将监听不到事件,后续使用会异常处理 public abstract void close() throws IOException;Channel
A nexus for I/O operations.
Channel 是针对IO操作的通道,用于数据的输入和输出,它和流之间的不同之处在于通道是双向的,而流是单向的,如流包含输入和输出流。下图为Chanel 类图,包含客户端的Chanel和服务端Channel,共同继承AbstractSelectableChannel、SelectableChannel,共同的接口为Channel。

ServerSocketChannel核心API
核心API功能介绍如下
/**创建一个ServerSocketChannel 函数*/
public static ServerSocketChannel open() throws IOException {
return SelectorProvider.provider().openServerSocketChannel();
}
/** 是否是一个有效的操作*/
public final int validOps() {
return SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT;
}
/**监听一个端口*/
public abstract ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local, int backlog)
throws IOException;
/**网络传输一些参数设置*/
public abstract <T> ServerSocketChannel setOption(SocketOption<T> name, T value)
throws IOException;
/**建立一个服务端连接*/
public abstract SocketChannel accept() throws IOException;
ServerSocketChannel核心API
核心API功能介绍如下
/**创建一个ServerSocketChannel 函数*/
public static ServerSocketChannel open() throws IOException {
return SelectorProvider.provider().openServerSocketChannel();
}
/** 是否是一个有效的操作*/
public final int validOps() {
return SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT;
}
/**监听一个端口*/
public abstract ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local, int backlog)
throws IOException;
/**网络传输一些参数设置*/
public abstract <T> ServerSocketChannel setOption(SocketOption<T> name, T value)
throws IOException;
/**建立一个服务端连接*/
public abstract SocketChannel accept() throws IOException;
/**
注册一个Channel事件到Selector
*/
public abstract SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att);
/**设置是否是堵塞IO*/
public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block);
SocketChannel核心API
核心API功能介绍如下
/**创建一个SocketChannel*/
public static SocketChannel open() throws IOException {
return SelectorProvider.provider().openSocketChannel();
}
/**是否是有效的操作*/
public final int validOps() {
return (SelectionKey.OP_READ
| SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
| SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
/**设置网络传输参数*/
public abstract <T> SocketChannel setOption(SocketOption<T> name, T value)
throws IOException;
/**判断是否和服务端进行连接*/
public abstract boolean isConnected();
/**判断是否和服务端正在连接*/
public abstract boolean isConnectionPending();
/**和服务端建立连接*/
public abstract boolean connect(SocketAddress remote) throws IOException;
/**判断是否和服务端进行完成连接,如果未完成,堵塞至完成连接*/
public abstract boolean finishConnect() throws IOException;
/**读取数据*/
public abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException;
/**写出数据*/
public abstract int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException;
/**注册一个Channel事件到Selector*/
public abstract SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att)
Buffer
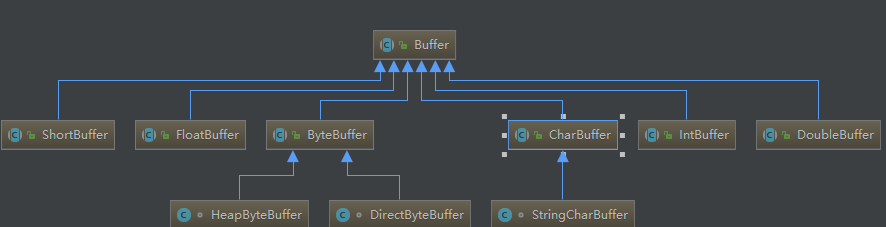
Buffer是一个缓存对象,所有的数据写入或写出都是先写入到Buffer对象,然后再通过Channel进行数据传输,而流方式是可以直接将数据写入到Stream对象中。Buffer内部本质就是一个数组,是一个抽象类,具体实现包含多种:ByteBuffer、IntBuffer、ShorBuffer、CharacterBuffer,同时也分为堆内和堆外等等。
Buffer类中三个核心属性:position、limit 以及capacity。position表示当前可以读或者可以写的起始点,limit表示不可读或不可以写的第一个下标,capacity则表示Buffer的容量大小。其中大小关系0<=position<=limit<=capacity。具体是如何使用的呢?现假如以读数据的场景来描述(写同理):
起初时:position值为0,limit和capacity值大小均是Buffer容量大小;
当不断进行数据读取时,此时position发生位置移动,而limit和capacity大小不变;
当需要读取出Buffer中数据时,需要进行数据flip反转,此时position变为0,limit变成之前position位置,limit-position区间表示可以读取的数据。

Buffer核心API
核心API功能介绍如下
// 表示上次读取或者写入的位置,作用是对当前调用mark函数时position位置记录
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;
/**记录当前position位置*/
public final Buffer mark() {
mark = position;
return this;
}
/**还原mark时position的值*/
public final Buffer reset() {
int m = mark;
if (m < 0)
throw new InvalidMarkException();
position = m;
return this;
}
/**将position、limit、capacity还原初始值*/
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
/**将limit设置position值,position值设置为0*/
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
/**position值设置为0*/
public final Buffer rewind() {
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
/**判断当前Buffer是否可读或者写的区间*/
public final int remaining() {
return limit - position;
}
/**判断当前Buffer是否可读或者写*/
public final boolean hasRemaining() {
return position < limit;
}
/**判断当前Buffer是否只能读*/
public abstract boolean isReadOnly();
/**判断当前Buffer是否是可可进入的Array*/
public abstract boolean hasArray();
/**判断当前Buffer转换为Array*/
public abstract Object array();
/**判断当前Buffer是否是直接Buffer*/
public abstract boolean isDirect();
SelectionKey
* A token representing the registration of a {@link SelectableChannel} with a* {@link Selector}.用于呈现一个Channle注册到Selector的令牌,具体表示其实就是表示一个Channel注册到Selector的事件,这个类同时绑定了Selector和Channel。
SelectionKey核心API
核心API功能介绍如下
/**关联的Channel*/ public abstract SelectableChannel channel(); /**关联的Selector*/ public abstract Selector selector(); /**当前key是否有效*/ public abstract boolean isValid(); /**取消对当前Channle的事件轮询*/ public abstract void cancel(); /**感兴趣的事件*/ public abstract int interestOps(); /**注册感兴趣的事件*/ public abstract SelectionKey interestOps(int ops); /**监听事件包含读、写、连接、接收一个连接*/ public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0; public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2; public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3; public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4; /**给当前事件绑定附加值*/ public final Object attach(Object ob) { return attachmentUpdater.getAndSet(this, ob); } /**当前事件绑定的附加值*/ public final Object attachment() { return attachment; }
JDK NIO实现Server-Client IO通讯案例
上面讲述了在java JDK层面实现NIO的一些核心类和相关的API,那如何将这些API串起来呢?现在采取上述API简单的实现一个客户端和服务端的通信案例。
服务端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 创建ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
//注册可建立连接的事件至Selector
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("Server started");
while (true) {
// Selector开始轮询Channel是否有就绪事件
int count = selector.select();
if (count > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
if (selectionKeys != null && selectionKeys.size() > 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
// 有可建立连接的事假
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 有就绪的Channel的读事件
else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.clear();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.read(buffer);
// 需要旋转至读取的数值
buffer.flip();
int cmdLength = buffer.getInt();
byte[] cdmBytes = new byte[cmdLength];
buffer.get(cdmBytes, 0, cmdLength);
String cmdStr = new String(cdmBytes, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
System.out.println("---111---" + cmdStr);
int contentLength = buffer.getInt();
byte[] contentBytes = new byte[contentLength];
buffer.get(contentBytes, 0, contentLength);
String contentStr = new String(contentBytes, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
System.out.println("---222---" + contentStr);
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 具备这个write事件后,才能attach值
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
selectionKey.attach("hello");
}
}
// 有就绪的Channel的写事件
else if (selectionKey.isWritable()) {
selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE & ~SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
System.out.println("-----------------");
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
String message = (String) selectionKey.attachment();
System.out.println(message);
int length = message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).length;
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.putInt(length);
buffer.put(message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
//表示相关事件已处理,需要清除,否则会重复读
selectionKeys.clear();
}
}
}
}
处理逻辑
- 开启Selector;
- 开启ServerSocketChannel;
- 注册为非堵塞,绑定ACCEPT事件;
- 循环轮询就绪的Key,进行Accept;
- 获取SocketChannel,注册非堵塞,绑定READ事件;
- 处理Read事件和注册写事件,进行输出。

客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 创建SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 注册连接事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
System.out.println("Client started");
while (true) {
int count = selector.select();
if (count > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
if (selectionKeys != null && selectionKeys.size() > 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
// 可连接事假
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {
socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
if(socketChannel.finishConnect()){
if(socketChannel.isConnected()){
System.out.println("connect");
String cmd="test";
String content="Hello";
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.putInt(cmd.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).length);
buffer.put(cmd.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
buffer.putInt(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).length);
buffer.put(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
}
// 可读事件
else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.clear();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()){
socketChannel.read(buffer);
// 需要旋转至读取的数值
buffer.flip();
int cmdLength= buffer.getInt();
byte[] cdmBytes=new byte[cmdLength];
buffer.get(cdmBytes,0,cmdLength);
String cmdStr=new String(cdmBytes, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
System.out.println("---receive---"+cmdStr);
}
}
}
//表示相关事件已处理,需要清除,否则会重复读
selectionKeys.clear();
}
}
}
}
处理逻辑
- 开启Selector;
- 开启ServerSocketChannel;
- 注册为非堵塞,绑定CONNECT事件;
- 循环轮询就绪的Key,进行connect;
- 对SocketChannel,绑定READ事件;
- 处理Read事件和注册写事件,进行输出。